Steps To Reformat A Personal Computer
#1 Start your pc and press key F2, F12 or delete key
(Depends on your PC model).
#2 Your PC will boot
from CD and windows installation will start. Press Enter at this screen.
#3 Accept License
agreement by pressing F8 key.
#4 Delete the partitions.
#5 Create the
partitions.
#6 Define the size of
partitions.
#7 Now select your
desired partition for installation of Windows XP and press enter.
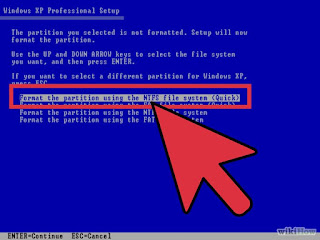
#8 Choose to format the
partition. Choose NTFS file system quick.
#9 Setup will format the
partition.
#10 After formatting,
setup will start copying files on to the hard disk.
#11 After copying of
files, setup will start installing Windows.
#12 Select desired
language and regional settings, when prompted by setup.
#13 Enter windows key.
#14 Type a name for your
computer.
#15 Select time and date
settings and time zone according to your country.
#16 Provide network
settings for networking pc's or select typical settings and press enter.
#17 Setup will install
devices and register components.
#18 After completion
setup will do a cleanup of files and will restart your pc
automatically. At this stage you can remove CD from drive.
To Create A Partition
What is disk partitioning?
Disk Partitioning is the creation of
one or more regions on a hard disk or other secondary storage,
so that an operating system can manage information in each region
separately.
Partitioning is typically the
first step of preparing a newly manufactured disk, before any files
or directories have been created.
Remember:
1 KB = thousand bytes
1
MB =
million bytes
1
GB =
billion bytes
1
TB =
trillion bytes
Remember:
1 KB = 1024 bytes
1
MB =
1024 KB
1
GB =
1024 MB
1
TB =
1024 GB
EXAMPLE:
Original size/capacity = 40995 MB
P1 - 50 % = 40995 x .50 = 20498
P2 - 50 % = 40995
x .50 = 20498
Original size/capacity = 40995 MB
P1 - 25 GB = 25 x 1024
=
25600
P2 - 25 % = 40995
x .25 = 10249
P3 - The rest
Original size/capacity = 38162
MB
P1 - 15 GB = 15 x 1024 =
15360
P2 - 30 % = 38162
x .30 = 11449
P3 - 100%
Original size/capacity = 38162
MB
P1 - 39 % = 38162
x .39 = 14883
P2 - 11 GB = 11 x 1024
= 11264
P3 - 100%
Original size/capacity = 40995 MB
P1 - 41 % = 40995 x .41 = 16808
P2 - 10 GB = 10 x 1024 =
10240
P3 - The
rest